Tasks are the tools GenoFAB uses to help people work together. They allow lab members to request, review and execute the work captured in the GenoFAB database.
Introduction
Up to this point, you have learned how to capture data in GenoFAB. Most laboratory information management systems and electronic lab notebooks leave it to users to properly record the work they have performed in the lab. They passively capture data and users tend to document their work long after it's been performed.
GenoFAB takes a more proactive approach. It allows lab members to request "stuff" by creating tasks associated with records. These requests can be reviewed and prioritized by the laboratory manager who assigns them to different lab members.
Tasks provide a measure of productivity in the lab. Because GenoFAB breaks down complex experimental workflows into simple tasks clearly associated with data, it makes it easier for everyone to figure out what needs to be accomplished next. As your team adopts GenoFAB, you should expect to see the number of tasks performed every month progressively increase.
Tasks are a way for teams to collaborate more effectively. Different members of the team can place requests that are reviewed and prioritized by a manager who will assign them to lab members based on their availability and qualifications. All the stakeholders get regular updates of the task status as jobs progress from request to delivery.
Relationships between tasks and records
Every catalog item is the product of work. People have to place and receive orders before they become available. People have to prepare growth media before they are available for cell culture. People have to run an experiment before the data becomes available for analysis.
Every item in your lab catalog is associated with a task corresponding to the work necessary to make the item available.
Items and their corresponding tasks follow parallel tracks corresponding to the progression from request to delivery.
The figure below uses a media preparation as an example.
The media preparation goes through four stages:
- Requested: someone requested to prepare a new batch of media.
- In progress: someone is working on the media preparation
- Available: The media preparation is available for use.
- Archived: The media preparation is exhausted and no longer available for starting new cultures.
- Canceled: This special status is used when a request is not completed.
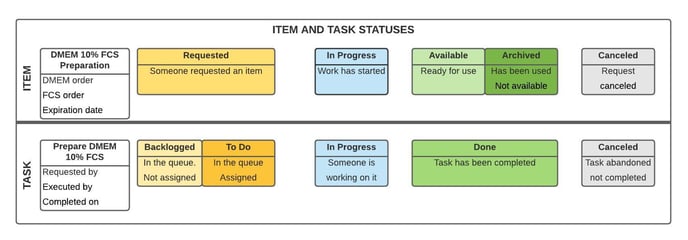
The task corresponding to the media preparation follows a similar life cycle.
- Backlogged: It's been requested but assigned yet.
- To Do: The task has been assigned to a user or group of users.
- In Progress: The media is being prepared.
- Done: The media preparation has been completed.
- Canceled: The media preparation was canceled.
Application
Tasks can be used to share work between different lab members. However, they can also be used by individual users to better manage their workload. This example uses the preparation of Fetal Calf Serum aliquots, a solution, to illustrate the relationship between tasks and records.
Requesting an item creates a task in backlog status.
In this demo account, we see there is no task in Backlog, Todo, or In progress status when the request is placed. Then the user requests an FCS preparation. This creates a new task in the backlog column.
Assigning tasks
In the next video, the lab manager assigns the task to a technician.
Processing tasks
In the next video, the technician logs in and picks up the task from her to-do list. Then she completes the task by making the corresponding item available.
Filling in the information relative to a request is usually something that needs to be executed in several steps as the corresponding operation progresses. A purchasing request for an instrument may require capturing a purchase order number first. Data such as the serial number or asset tag number are captured after the task has been completed.
Canceling tasks
Tasks that cannot be completed can be canceled. See this article for details.
